
|
GENTAUR EUROPE BELGIUM1 tel +32 2 732 5688 fax +32 2 732 4414 [email protected] Av. de l' Armée 68 B-1040 Brussels France tel 01 43 25 01 50 fax 01 43 25 01 60 9, rue Lagrange 75005 Paris Italy tel 02 36 00 65 93 fax +32 16 50 90 45 20135 Milano Germany tel +32 16 58 90 45 fax +32 16 50 90 45 Forckenbeckstraße 6 D-52074 Aachen Japan tel +81 78 386 0860 fax +81 78 306 0296 Minaatojimaminami-manchi Chuo-ku, Kobe 065-0047 |
Stabil-P.A.C. NV10 Removal
NVoy polymers interact with hydrophobic patches on a
protein forming a polymer : protein complex in dynamic
equilibrium with the free polymer in solution. NV10 can be removed from a
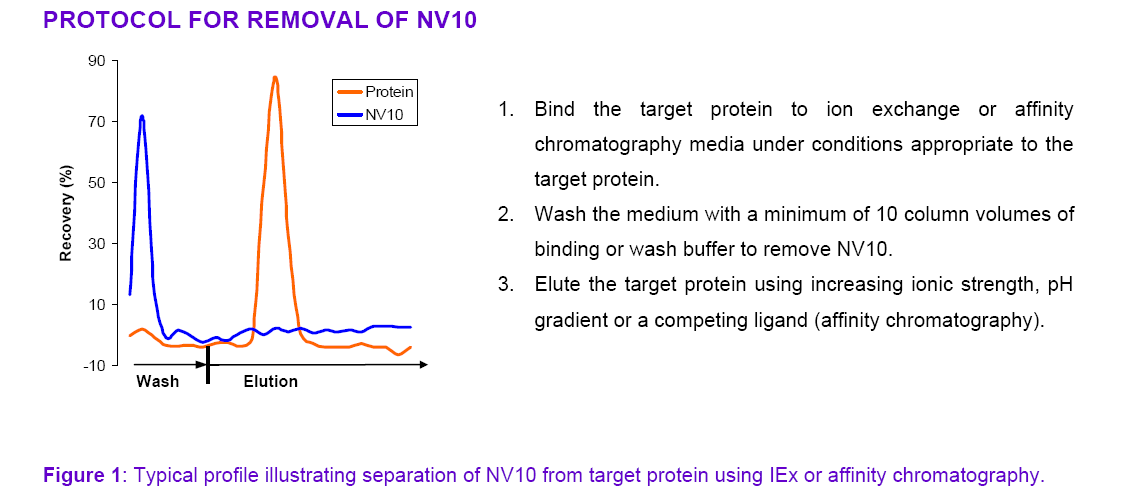
protein solution by binding the target
protein to ion-exchange or affinity media and washing out NV10 before elution of
the target protein.
Ion exchange chromatography (IEx) is a technique whereby a charged protein can
reversibly interact with an
oppositely charged matrix, and then be eluted by a change in buffer ionic
strength or pH. Each protein is composed
of a unique combination of individual amino acids, and different proteins
therefore often have differing net charges
at any given pH.
• The pH at which a protein has no
net charge is termed the iso-electric point (pI).
• The pI of a protein should be
determined experimentally, but if the amino acid sequence is known then the
theoretical
pI can be estimated at websites such as
http://us.expasy.org/tools/ .
• Under conditions where the pH is
higher than the pI the protein will have a net negative charge, and bind to
an anion
exchange resin (positively charged).
• Under conditions where the pH is
lower than the pI the protein will have a net positive charge and bind to a
cation
exchange resin (negatively charged).
Affinity chromatography is a method of separating a mixture of proteins by
utilizing specific interactions of the target
protein with a ligand which is immobilized on a support, eg IMAC, Protein A.
Troubleshooting
In most cases the target
protein will bind as normal to the resin of choice. If the binding is weaker
than expected
the interaction with the solid phase can be enhanced using a release agent to
weaken the interaction between the
protein and NV10 polymer. Novexin supplies these release agents as part of
Stabil-P.A.C.:
• Addition of dimethylsulfoxide
(DMSO) will facilitate a slow gentle release.
• Addition of “NV10 removal solution”
will facilitate instantaneous release.
PROTOCOL FOR RELEASE OF NV10
1. Determine quantity of NV10 in solution.
2. Up to 10 % of release agent
(either DMSO, or 1X removal agent) may be added to a 1X solution of NV10
(2.5 mg/ml).
3. Incubate for 10 minutes room
temperature.
4. Perform NV10 removal using IEx or
affinity chromatography.
Note! A protein which is intrinsically
prone to aggregation or instability may precipitate at this point.
Troubleshooting
If a heavy protein precipitate forms at the release step:
• Use DMSO as a release agent rather
than “NV10 removal solution” to give a more gentle dissociation of
components.
• Add less release agent.
• Add release agent in small aliquots
over a longer period of time.
• Perform release at 4 oC.
If NV10 is still present in the protein sample after release and removal:
• Extend column chromatography wash
step to 20 column volumes before protein elution.
• Add 10 % DMSO to the IEx or
affinity wash buffer before protein elution.

