
|
GENTAUR EUROPE BELGIUM1 tel +32 2 732 5688 fax +32 2 732 4414 [email protected] Av. de l' Armée 68 B-1040 Brussels France tel 01 43 25 01 50 fax 01 43 25 01 60 9, rue Lagrange 75005 Paris Italy tel 02 36 00 65 93 fax +32 16 50 90 45 20135 Milano Germany tel +32 16 58 90 45 fax +32 16 50 90 45 Forckenbeckstraße 6 D-52074 Aachen Japan tel +81 78 386 0860 fax +81 78 306 0296 Minaatojimaminami-manchi Chuo-ku, Kobe 065-0047 |
Determination of Protein Concentration
Several
methods are commonly used for determination of protein concentration.
Measurement of the UV
absorbance at 280 nm is most useful for pure protein solutions. Bradford and BCA
assay methods are routinely
used during protein purification and screening. Novexin has developed a novel
assay formulation, Bradford
ULTRA, with the features of the standard Bradford assay and the added advantage
of greater tolerance of
detergents.
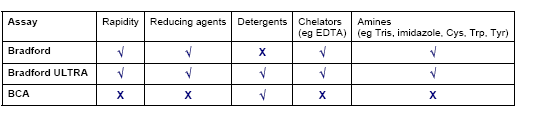
Table 1: Comparison of Bradford, Bradford ULTRA and BCA protein assay methods.
PROTEIN DETERMINATION USING ABSORBANCE AT 280 nm
(Ref: Pace, C.N. et al, (1995) Protein Sci,. 4, p2411.)
If a protein sequence is known, the theoretical extinction co-efficient at 280
nm, ε280nm, can be estimated using the
equation
ε280nm (M-1cm-1) = (#Trp)(5500)+ (#Tyr)(1490)+(#Cys)(125)
• Warm up the UV lamp (about 15 min).
• Zero spectrophotometer to buffer at 280 nm in a quartz
cuvette.
• Measure the absorbance of protein solution at 280 nm in a
quartz cuvette.
• Protein concentration is calculated as:
[Protein]
(mg/mL) = A280nm /(ε280nm x (cuvette path length in cm))
Note! An economical and disposable alternative to
quartz cuvettes are cuvettes made from optical grade polymethyl
methacrylate (PMMA), eg Fisher Scientific, Disposable UV Cuvettes, #CXA-205
series.
NVoy technology is a quantum leap in protein processing, production and
analysis. It uses
proprietary NV polymers to enhance protein solubility and stability through the
formation of
multi-point reversible complexes with proteins without altering their structure.
PROTEIN DETERMINATION USING THE BRADFORD ASSAY
(Ref. Bradford, M. M. (1976) Anal. Biochem. 72, p248.)
The Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 dye binds selectively to positively charged
residues (lysine, arginine and
histidine) and aromatic residues, and this binding is accompanied by a shift in
absorbance maximum from 465 nm
to 595 nm. The assay is fast, inexpensive and sensitive, and tolerates a wide
range of buffers. The Bradford assay
is, however, protein dependant, non-linear and detergent incompatible. Novexin
has developed a detergent
compatible assay solution, Bradford ULTRA, which removes the requirement for
detergent-solubilised protein to be
precipitated before use.
Note! The Coomassie dye binds to quartz, so it is advisable to use glass
or plastic cuvettes.
PROTOCOL for Bradford ULTRA
• Mix the Bradford ULTRA Reagent solution immediately before
use by gently inverting the bottle several times
(Do not shake the bottle to mix the
solution). Remove the amount of reagent needed and equilibrate it to room
temperature before use.
• Make a dilution series of the chosen
model protein in the range:
0.1 mg/ml – 1.5 mg/ml (high protein
range) OR
1 μg/ml – 25 μg/ml (low protein
range)
• Mix the samples, standards and a blank (buffer, no protein)
with Bradford ULTRA reagent in a microtiter plate:
o For 0.1
mg/ml – 1.5 mg/ml protein (high range): 20 μl sample + 300 μl Bradford ULTRA
reagent.
o For 1 μg/ml
– 25 μg/ml protein (low range): 150 μl sample + 150 μl Bradford ULTRA reagent
• Read absorbance immediately at 595 nm.
• Subtract the average 595 nm measurement for the blank from
the 595 nm measurements of all other
individual standards and unknown
samples. Plot the average blank-corrected 595 nm measurement for each
standard vs. concentration. Use the
slope of this standard curve to estimate the protein concentration of the
unknown samples.
NVoy technology is a quantum leap in protein processing, production and
analysis. It uses
proprietary NV polymers to enhance protein solubility and stability through the
formation of
multi-point reversible complexes with proteins without altering their structure.
PROTEIN DETERMINATION USING THE BCA ASSAY
(Ref. P.K. Smith et al. (1985) Anal. Biochem. 150, p76.; K. J.
Wiechelman et al. (1988) Anal. Biochem. 175, p231.)
This is a two-step assay, in which Cu2+ is first reduced to Cu1+ forming a
complex with protein amide bonds (Biuret
reaction). Secondly, bicinchoninic acid (BCA) forms a purple complex with Cu1+
which is detectable at 562nm. The
assay is sensitive and linear but is relatively slow unless heated.
PROTOCOL for BCA Assay
Reagent A:
• 1 g bicinchoninate (BCA), 2 g sodium carbonate, 0.16 g sodium tartrate, 0.4 g
NaOH,
0.95 g sodium bicarbonate.
• Mix reagents in 80 ml distilled water, adjust pH to 11.25 with 8 M NaOH, and
make
solution up to 100 ml.
Reagent B: • 4% CuSO4.5H2O (4 g in 10 ml distilled water).
Working solution (WS):
• Mix 50 volumes of Reagent A with 1 volume of Reagent B.
• This green solution is stable for 1 week.
• Make a dilution series of the chosen model protein
(eg BSA, IgG) as 100 μL samples containing 0 - 100 μg
protein
• Add 2 ml of WS to each 100 μL sample or standard.
• Seal samples and incubate at 60 oC for 15 minutes (or 37 oC for 30 minutes).
• Cool samples to room temperature and measure the absorbance at 562 nm.
• Subtract the average 562 nm blank from the 562 nm measurements of all other
standards and samples. Plot the
average, blank corrected measurement for each standard vs.
concentration. Use the slope of this standard curve
to estimate the protein concentration of the unknown samples.

