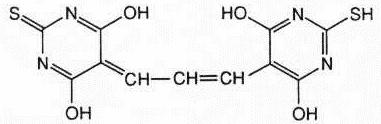(TBARS) ASSAY
Thiobarbituric Acid
Reactive Substances
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR in
vitro DIAGNOSTIC USE.
| |
|
|
INTENDED
USE |
|
The
sensitivity of measuring Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive
Substances (TBARS) has made this assay the method of choice
for screening and monitoring lipid peroxidation, a major
indicator of oxidative stress (1-3). This rapid,
easy-to-use procedure has been modified by researchers for
use with many types of samples including drugs, food
products and human and animal biological tissues (4-7)
. The assay has provided important information regarding
free radical activity in disease states and has been used
for measurement of anti-oxidant activity of several
compounds (8-9) . Although much controversy has
appeared in the literature regarding the specificity of
TBARS toward compounds other than MDA, it remains the most
widely employed assay used to determine lipid peroxidation
(10) . If lipoprotein fractions are first acid
precipitated from the sample, interfering soluble TBARS are
minimized. Nonetheless, if TBARS are increased, it is
recommended that a more specific assay such as HPLC be
performed.
The OXItek TBARS Kit is designed to
provide a standardized, reproducible assay with consistent
results. Each lot of reagents is quality controlled as a
kit, which includes an MDA standard. It is recommended that
additional in-house controls are included in each test run.
The OXItek TBARS Assay Kit is
for Research Purposes Only.
|
| |
|
|
PRINCIPLES OF
THE SYSTEM |
|
Malondialdehyde
(MDA) forms a 1:2 adduct with thiobarbituric acid and
produces the following:
which can be measured by fluorometry
or spectrophotometry. Although this reaction has a much
higher sensitivity when measured via fluorometry, protocols
for both methods are provided in the Test Procedure section
of this insert.
Biological specimens contain a mixture
of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS),
including lipid hydroperoxides and aldehydes, which increase
as a result of oxidative stress. TBARS return to normal
levels over time, depending upon the presence of
anti-oxidants. In practice, TBARS are expressed in terms of
malondialdehyde (MDA) equivalents (11) . In this
assay, an MDA standard is used to construct a standard curve
against which unknown samples can be plotted.
The OXItek TBARS Assay Kit provides
all the necessary reagents to perform 160 tests and is
designed for researchers studying oxidative stress and
anti-oxidant activity. It is recommended that in-house
controls be run with each sample test.
Depending on geographic location, normal
plasma and serum TBARS should be <1.5 and <2.0 MDA units
respectively. Mean and ± SD or SE must be established by
each laboratory. It is recommended that samples be run in
duplicate
Limitation
to Procedure:
1. Hemolyzed, icteric or
lipemic plasma samples are not suitable for use in TBARS
analysis.
2. Non-lipid TBARS may be present in the sample. It is
recommended that a sample with elevated TBARS levels be
tested by a more specific test for lipid peroxidation such
as HPLC.
3. Normal tissues contain very low levels of free
malondialdehyde
|
| |
|
|
|
REAGENTS |
|
Materials Supplied:
• Thiobarbituric Acid (4
vials/kit): Contains 0.53 grams thiobarbituric acid
• TBA
Diluent 1 (4 x 50 ml/kit) : Contains acetic acid
• TBA
Diluent 2 (4 x 50 ml/kit): Contains sodium hydroxide
• SDS
Solution (30 ml/kit): Contains sodium doedecyl sulfate
• MDA
Standard (10 ml/kit): Contains100nmol/ml Malondialdehyde
Bis (dimethyl acetal)
• MDA Diluent
(100 µl/kit):
Marbles
Storage:
Store all kit
reagents at 2-8 ° C. The components should
be used before the expiration date indicated on the outside
of the box.
Materials
Required but not Supplied:
• 12 x 75 mm glass test tubes and metal
racks
• Disposable gloves
• Adjustable pipettes
• Graduated cylinders and assorted beakers
• Stir plate
• Heat block, incubator or water bath set
at 95 ° C
• Fluorometer or Spectrophotometer
|
| |
|
|
|
PRECAUTIONS |
|
- To avoid cross
contamination, use separate pipette tips for each
specimen.
- TBA Diluent 1 contains
acetic acid. Handle and dispose of according to
applicable legal and safety guidelines.
- TBA Diluent 2 contains
sodium hydroxide. Handle and dispose of according to
applicable legal and safety guidelines.
- If reusing glass tubes,
be certain to rinse thoroughly in deionized water.
|
| |
|

|
PREPARATION
OF REAGENTS |
|
Note:
Prepare fresh for each analysis.
TBA/Buffer
Reagent:
Use 1 bottle of TBARS Diluent 1 (50
ml), 1 bottle of TBARS Diluent 2 (50 ml) and 1 vial of
Thiobarbituric Acid (TBA). One hundred ml is sufficient for
approximately 40 tubes.
Add TBA to a mixing vessel
containing half a bottle of TBARS Diluent 1. Rinse the vial
with the remaining half of TBARS Diluent 1 and add to the
mixing vessel. Add a full bottle of TBARS Diluent 2. Mix
until the TBA is completely dissolved. If necessary, very
low heat may be used.
MDA Standard
For Fluorometer:
Dilute MDA
Standard 1:10 by mixing 1.8 ml of MDA Diluent and 0.2 ml of
MDA Standard. Mix thoroughly. Prepare a series of 5
standards in MDA Diluent. The dilution scheme for these
standards is given below in Table 1.
Table
1: Preparation of MDA Standard For Fluorometer
|
Standard
Number
|
Concentration of MDA
|
Volume
of MDA Standard
|
Volume
of Diluent
|
|
4
|
4 nmol/ml
|
400 µl
|
600 µl
|
|
3
|
3 nmol/ml
|
300 µl
|
700 µl
|
|
2
|
2 nmol/ml
|
200 µl
|
800 µl
|
|
1
|
1 nmol/ml
|
100 µl
|
900 µl
|
|
0
|
0 nmol/ml
|
0 µl
|
1000 µl
|
* The concentration of the
1:10 standard is 10 nmol/ml, and may be used directly as
an additional standard when assaying samples expected to
have elevated TBARS, such as urines.
MDA Standard
For Spectrophotometer:
Use MDA
Standard undiluted for 100 nmol/ml standard. Prepare a
series of 5 standards in MDA Standard Diluent. The dilution
scheme for these standards is given below in Table 2.
Table 2:
Preparation of MDA Standard For Spectrophotometer
|
Standard
Number
|
Concentration of MDA
|
Volume
of MDA Standard
|
Volume
of Diluent
|
|
4
|
100 nmol/ml
|
1000 µl
|
0 µl
|
|
3
|
50 nmol/ml
|
500 µl
|
500 µl
|
|
2
|
25 nmol/ml
|
250 µl
|
750 µl
|
|
1
|
12.5
nmol/ml
|
125 µl
|
875 µl
|
|
0
|
0 nmol/ml
|
0 µl
|
1000 µl
|
|
| |
|
|
TEST
PROCEDURE |
|
Allow all reagents to reach room temperature before use. SDS
Solution will take at least one hour if stored at 2-8 ºC.
Heating the SDS Solution will redissolve precipitated SDS.
SDS Solution can then be stored at room temperature.
Step 1: Collect EDTA plasma
(lavender top Vacutainer®). For preparation of
other sample types, see sample preparation section of this
insert.
Step 2: Label each
disposable glass test tube with the standard number or
sample identification.
Step 3: Add 100 µl sample
or standard to properly labeled tube.
Step 4: Add 100 µl SDS
Solution to each tube and swirl to mix.
Step 5: Add 2.5 ml TBA/Buffer Reagent forcefully
down the side of each tube.
Step 6: Cover each tube with a glass marble and
incubate at 95ºC for 60 minutes.
Step 7: Remove from incubation and cool to room
temperature in an ice bath for 10 min.
Step 8: Centrifuge samples at 3000 rpm for 15
minutes.
Step 9: Remove supernatant from samples for
analysis.
Step 10: Fluorescent
Analysis: read supernatants with excitation set at
530 nm and emission at 550 nm. It is recommended sensitivity
be set at high with a slit width of 5 nm.
Spectrophotometer
Analysis: Read absorbance of supernatants at 532 nm.
|
| |
|
|
SAMPLE
PREPARATION |
|
Note:
Samples should be tested immediately. If serum/plasma
samples are not tested immediately, remove from clot,
aliquot and store at -70° C.
Platelets:
Collect 5 ml
specimen of heparinized venous blood (green top
Vacutainer®) from patients who have fasted
overnight. Remove stopper and let RBCs sediment by
gravity. Pipet off platelet-rich plasma (PRP) into
clean, plastic centrifuge tube after 1 ml has formed and
continue until separation is complete. Centrifuge PRP at
1400 rpm for 5 min, collect supernatant and centrifuge
the supernatant at 5000 rpm for 15 min to sediment
platelets.
Leukocytes:
Collect blood in EDTA (lavender top
Vacutainer®). Allow RBCs to sediment; collect
upper "Buffy Coat".
Wash leukocytes contained in the Buffy Coat once in an
isotonic solution such as saline or Dulbecco’s PBS.
Resuspend leukocytes in isotonic solution for testing(15).
Erythrocyte Ghosts:
Wash RBC pellet from
leukocyte separation with 20 ml of TRIS Buffer, pH 7.4
(6.05 g TRIS, 6.42 g NaCl, 420 ml 0.1M HCl, 580 ml
deionized water), centrifuge at 3500 rpm for 10 minutes,
discard supernatant and repeat twice. Add an equal
volume of TRIS Buffer to final pellet and incubate a
minimum of 4 hours at 4 ºC. Lysis of erythrocytes is
performed on ice with pre-cooled conditions. Add 15 ml
lysing solution (301 mg MgSO4,
372 mg KCl in 500 ml of sterile water) to 0.5 ml of the
cell suspension. Immediately add 1 ml of resealing
solution (53.7 g KCl, 10.5 g NaCl in 400 ml of deionized
water). Keep the suspension on ice for 5 mn and then at
37 ºC for 30 min. Pellet the ghosts by centrifuging for
10 min at 3500 rpm(12) .
Oxidized LDL:
Plasma: Collect fasting
heparinized whole blood. Centrifuge at 3500 rpm for 10
minutes at 5-10ºC, carefully remove plasma and place on
ice for immediate analysis or freeze several aliquots at
-70 ºC for later analysis. Samples can be safely stored
for 1-2 months. Process as described below for serum(3).
Serum: Collect fasting whole
blood in a red top vacutainer®.. Incubate at
room temperature for at least 30 minutes for clots to
form. Centrifuge at 3500 rpm for 10 minutes. Carefully
remove serum and place on ice for immediate analysis or
freeze aliquots at -70 ºC for later analysis. Add 1.5 ml
of isotonic saline to 1.5 ml of plasma/serum. Prepare a
sodium heparin solution in water containing 40,000 USP
units per ml. Prepare a solution of 1.06M manganese
chloride in water. A working reagent is prepared with
300 µl sodium heparin solution to 5 ml manganese
chloride solution. Scale up as necessary. Add 300 µl of
working reagent to the diluted serum/plasma. Vortex and
allow the LDL/VLDL to precipitate for 15 min at room
temperature. Centrifuge the serum/plasma at 8000 rpm for
15 min. Decant the serum/plasma supernatant and
resuspend the pellet in 1.5 ml normal saline or PBS(3,13)
. If required, sonicate each sample 5 sec at low setting
over ice. Use these samples to start the TBARS assay,
substituting water for SDS in the reaction mixture.
Note: When analyzing
samples that may be non-fasting, triglycerides measuring
above 300-350 mg/dL will yield a turbid supernatant and
cannot be measured.
Other Body Fluids:
The TBARS kit is suitable for analysis of CSF,
vaginal, synovial, seminal, vitreous, tears, saliva,
sperm, pulmonary and gastrointestinal fluids and
lavages.
Tissues:
Freeze tissue in liquid
nitrogen and immediately crush in a pre-chilled mortar
and pestle. Resuspend tissue at 50 mg/ml in normal
saline or PBS. Disrupt in a Potter-Elvejhem glass
homogenizer. If necessary, sonicate for 15 sec at
40V setting over ice and use uncentrifuged whole
homogenate for analysis. Alternatively, homogenize in
isotonic media appropriate for sub-cellular
fractionation to study TBARS in plasma membranes,
nuclear membranes or
organelles. Spun
supernates may be used for enzyme analyses. Recommend
normalizing TBARS values to another constituent such as
protein.
Cell Cultures:
Suspend 20 million cells
in 1 ml of cell culture medium or buffer of choice such
as PBS. Sonicate for 5 second intervals at 40 V setting
over ice. Use whole homogenates in the assay, being sure
to use culture fluid as a sample blank.
Anti-Oxidant Screening:
The TBARS assay may be
used for testing anti-oxidants and drugs
(13). Oxidize 2 100 µl aliquots of a
sample, such as serum or plasma, with 5mM ferric
chloride. Add the anti-oxidant compound to be tested to
one. Incubate plasma alone plus the 2 test samples at 37ºC
for 30 min and compare to distilled water control.
Calculate percentage of inhibition(14)
. Drugs may be added directly to plasma samples
and compared to plasma alone in the TBARS assay
|
| |
|
|
CALCULATIONS
AND
INTERPRETATION
OF RESULTS |
|
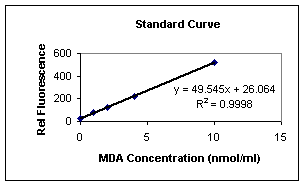
Typical Standard Curve (Fluorometer):
This is an example of a typical standard curve and is not to
be used for interpretation of results. Variation may occur
in individual laboratories due to pipetting, laboratory and
incubator temperatures, etc.
Table 3:
Sample Standard Curve
|
MDA
Concentration
|
Fluorometer
Readings
|
|
10nmol/ml
|
521.15
|
|
4nmol/ml
|
223.68 |
|
2nmol/ml
|
126.48
|
|
1nmol/ml
|
78.69
|
|
0nmol/ml
|
22.5
|
For Fluorometer:
Using linear graph paper, plot mean MDA equivalents for
each standard used on the X-axis versus the
corresponding fluorometer reading on the Y-axis.
Determine the concentration of MDA equivalents in
nmol/ml in specimens by interpolation from the standard
curve. Correct sample values for any other dilutions
performed during specimen preparation.
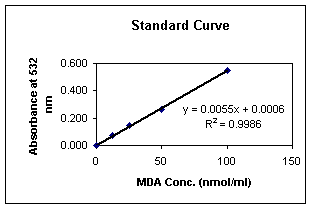
Typical Standard Curve (Spectrophotometer):
This is an example of a typical standard curve and
is not to be used for interpretation of results. Variation
may occur in individual laboratories due to pipetting,
laboratory and incubator temperatures, etc.
Table 4: Sample Standard
Curve
|
MDA
Concentration
|
Spectrophotometer Readings
|
|
100
nmol/ml
|
0.550
|
|
50
nmol/ml
|
0.260
|
|
25
nmol/ml
|
0.145
|
|
12.5
nmol/ml
|
0.070
|
|
0
nmol/ml
|
0.000
|
For
Spectrophotometer:
Using linear graph
paper, plot mean MDA equivalents for each standard used
on the X-axis versus the corresponding spectrophotometer
reading on the Y-axis. Determine the concentration of
MDA equivalents in nmol/ml in specimens by interpolation
from the standard curve. Correct sample values for any
other dilutions performed during specimen preparation.
Graph 2
|
| |
|
|
|
REFERENCES |
|
- Yagi, K.
Simple procedure for specific assay of lipid
hydroperoxides in serum or plasma. Free Radical and
Antioxidant Protocols, 108: 101-106;1998
-
Armstrong, D. and Browne, R. The analysis of free
radicals, lipid peroxidases, antioxidant enzymes and
compounds related to oxidative stress as applied to the
clinical chemistry laboratory. Free Radicals in
Diagnostic Medicine, 366:43-58;1994
- Lef’evre
G., et.al. Evaluation of lipid peroxidation by measuring
thiobarbituric acid reactive substances. Annals de
Biologie Clinique (Paris) May-June; 56(3):305-19; 1998
- Janero,
D. Malondialdehyde and thiobarbituric acid-reactivity as
diagnostic indices of lipid peroxidation and
peroxidative tissue injury. Free Radical Biology &
Medicine, 9:515-540; 1998
-
Callaway, J.K. et. al. A reliable procedure for
comparison of antioxidents in rat brain homogenates.
Journal of Pharmacology Toxicology Methods, April;
39(3):155-62; 1998
- Jentzsh,
AM., et. al. Improved analysis of malondialdehyde in
human body fluids. Free Radio Biol Med., 20(2):251-6;
1996
- Jo, C.
et. al. Fluorometric analysis of 2-thiobarbituric acid
reactive substances in turkey. Pout. Sci., March;
77(3):475-80; 1998
-
Villa-Caballero, L. et. al. Oxidative Stress. Should it
be measured in the diabetic patient? Gac Med Mex,
May-June; 136(3):249-56; 2000
-
Hunnisett A. et. al. Lipoperoxides as an index of free
radical activity in bone marrow transplant recipients.
Preliminary Observations. Biol Trace Elem Res,
Jan-March; 47(1-3):125-32; 1995
-
Armstrong, D. and Browne, R. The analysis of free
radicals, lipid peroxidases, antioxidant enzymes and
compounds related to oxidative stress as applied to the
clinical chemistry laboratory. Free Radicals in
Diagnostic Medicine, 366:46; 1994
- Kwon,T.
and Watts,B. Malonaldehyde in aqueous solution and its
role as a measure of lipid oxidation in foods. Journal
of Food Science, 29:294-302; 1964
- Braun,D.
and Fromherz,P. Fluorescence interference-contrast
microscopy of cell adhesion on oxidized silicon. Applied
Physics A, 1997
- Gidez,L.
et al. Separation and quantitation of subclasses of
human plasma high density lipoproteins by simple
precipitation procedure. Journal of Lipid Research,
23:1206-1223; 1982
-
Armstrong,D. et al. In vitro screening for antioxidant
activity.Free Radical and Antioxidant Protocols,
108:315-324; 1998
- Boyum,
A. Separation of leukocytes from blood and bone marrow.
Scandinavian Journal of Clinical Investigation 21,
Supplement 97; 1966.
|
| |
|
|
PROCEDURAL
FLOW CHART |
|
PREPARE REAGENTS
PIPET
SPECIMENS AND CONTROLS
ADD SDS
SOLUTION
ADD
TBA/BUFFER REAGENT
INCUBATE 60
MIN AT 95º ±1º C
COOL TO ROOM
TEMPERATURE
CENTRIFUGE
SPECIMEN
READ RESULTS
* The OXI-TEK TBARS Assay Kit is
for Research Purposes Only.
|
|